LED UV curing has become a mainstream option for narrow-web and label production. Advances in diode technology and curing chemistry now allow flexographic presses to achieve faster runs, lower waste, and improved safety. This review focuses on practical performance aspects for labels, flexo plates, letterpress-style systems, and narrow-web installations. Technical details, integration considerations, and real-world trade-offs are covered.
How LED UV curing works in flexo
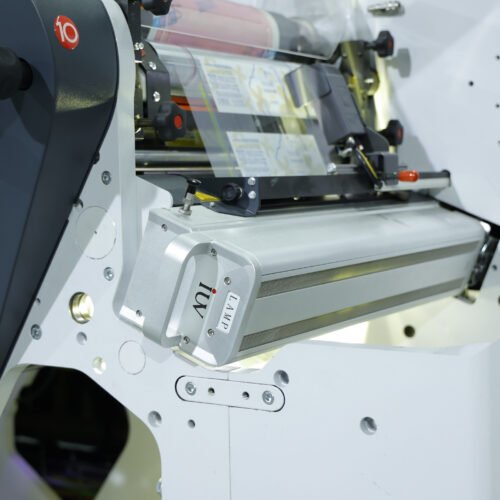
LED UV systems use arrays of light-emitting diodes that emit narrowband ultraviolet light, most commonly near 365, 385, 395, or 405 nm wavelengths. Photoinitiators in inks and coatings absorb this energy and trigger rapid polymerization. Compared with mercury arc lamps, LEDs provide instant on/off control, stable output, and much lower heat emission toward the print web. The narrow spectral output demands matched ink formulations and photoinitiator packages to ensure complete cure.
Key performance metrics
Cure speed: Measured in millijoules per square centimeter (mJ/cm²) at target wavelengths. Effective cure depends on dose, intensity, and exposure time across the web width. In narrow-web label presses, short dwell times require high intensity and optimized lamp placement.
Adhesion and gloss: Properly formulated UV-LED inks deliver adhesion and gloss on par with traditional UV, when the photoinitiator system matches the LED emission spectrum.
Through-cure and tack: Through-cure prevents migration, blocking, and tack on rewind. Monitoring surface and bottom tack with test strips is standard practice after retrofit or ink change.
Heat load: LEDs reduce radiant heat significantly compared with mercury lamps. This benefits heat-sensitive substrates, narrow cores, and processes requiring close ink stacking.
Energy consumption and lifecycle: LEDs consume less power for equivalent curing output. Diode life exceeds several thousand hours with predictable lumen depreciation. Fans and drivers still require consideration for total system energy.
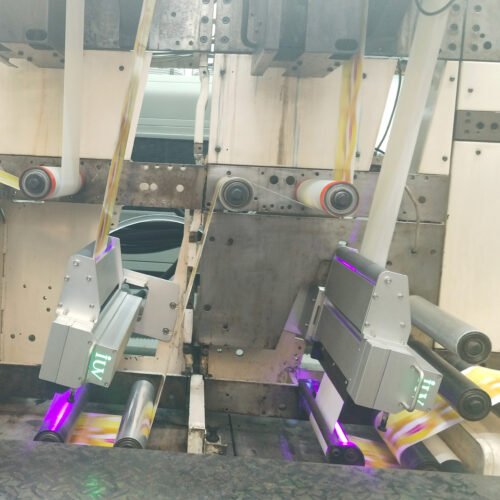
Label printing and narrow-web considerations
Labels demand consistent color, strong adhesion on diverse substrates, and wrinkle-free rewinding. LED UV is especially attractive where thermal stress must be minimized, such as on thin films, thermal papers, or shrink-sleeve substrates. Narrow-web presses often operate at high linear speeds with limited exposure length. Lamp modules with concentrated intensity and reflector optimization help deliver required doses within short exposures.
Common substrate scenarios:
- BOPP film: Lower heat absorption reduces web distortion. Choose inks with high migration resistance for adhesive compatibility.
- Paper stock: Moisture content and calendering affect ink anchorage. LED curing supports reduced set-off and instant handling.
- Shrink sleeves: Uniform cure across film thickness is needed to avoid post-shrink stress. Proper ink formulation and dose control are key.
Ink and photochemistry compatibility
Successful LED conversion requires ink and varnish systems designed for the LED emission band. Conventional UV inks using broad-spectrum photoinitiators may underperform under LED output. Formulators supply LED-specific photoinitiators and coinitiators to improve polymerization rates and surface hardness.
Selecting inks:
- Verify spectral response: Request spectral sensitivity data from ink suppliers.
- Test tack and adhesion: Run press trials across expected substrates and environmental conditions.
- Consider flexo plate interaction: Ink transfer characteristics can change with cure speed differences. Adjust anilox roll selections if needed.
Effect on plate and rubber blanket systems
Flexographic plates and rubber rollers see less thermal loading with LED systems. Reduced heat can extend plate life and stabilize impression settings. However, quicker cure speeds may alter ink rheology during transfer. Plate exposure and relief design continue to matter, but operators may fine-tune impression pressure and anilox volumes to match new cure dynamics.
Retrofit and integration issues
Retrofitting existing presses with LED modules often provides rapid return on investment, but several integration factors affect performance:
- Mechanical fit: Lamp module dimensions must align with hood and web path constraints.
- Cooling and ventilation: LEDs generate focused heat at the diode and driver, requiring proper heat sinking and air management.
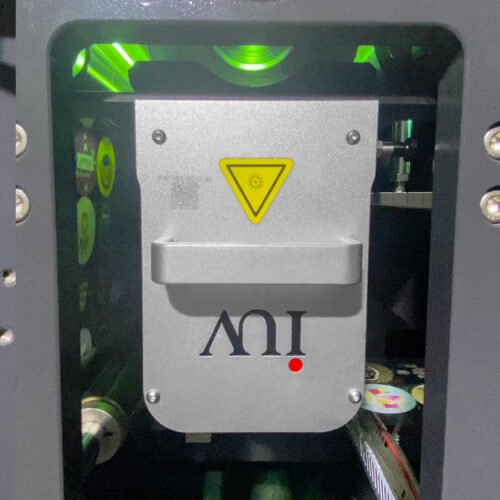
- Safety interlocks: Guards, shields, and interlocks must meet local regulations for UV exposure.
- Controls and monitoring: Integrated dimming, zone control, and dose meters improve consistency.
- Electrical considerations: LED systems typically require DC drivers with stable voltage and current. Check press power availability and harmonics.
Routine maintenance differs from mercury systems. There are no bulb changes, but periodic cleaning of reflectors and lens surfaces maintains output. Driver electronics should be checked on service intervals.
Operational benefits and limitations
Benefits:
- Lower web temperature reduces substrate distortion and shrinkage.
- Instant on/off reduces startup waste and short-run inefficiencies.
- Reduced ozone and hazardous emissions improve shop environment and decrease ventilation demands.
- Extended diode lifetime lowers lamp replacement frequency and reduces consumable costs.
Limitations:
- Need for LED-compatible ink and coating formulations.
- Potential for incomplete cure if spectrum or dose is mismatched.
- Capital cost for retrofit can be significant for larger installations.
- Narrow spectral band can expose formulation weaknesses otherwise masked by broad-source lamps.
Best practices for pressroom adoption
- Conduct comprehensive ink trials on representative substrates and under full-speed conditions.
- Use a dose-meter and spectroradiometer to verify energy delivery at the web surface.
- Work with ink and lamp vendors to match photoinitiator chemistry to lamp wavelength and intensity.
- Adjust anilox, impression settings, and drying profiles to the new cure regime.
- Implement sampling protocols to monitor surface tack, adhesion, and migration in real production.
- Train operators on dose control, preventive lens maintenance, and safety procedures around UV exposure.
Conclusion
LED UV curing delivers compelling advantages for flexographic label and narrow-web production. The technology reduces thermal load and energy use while supporting higher press uptime and lower waste. Realizing full performance requires matched chemistries, careful retrofit planning, and methodical testing across substrates and inks. With those elements addressed, LED systems can raise productivity and stability for modern label and flexo operations.