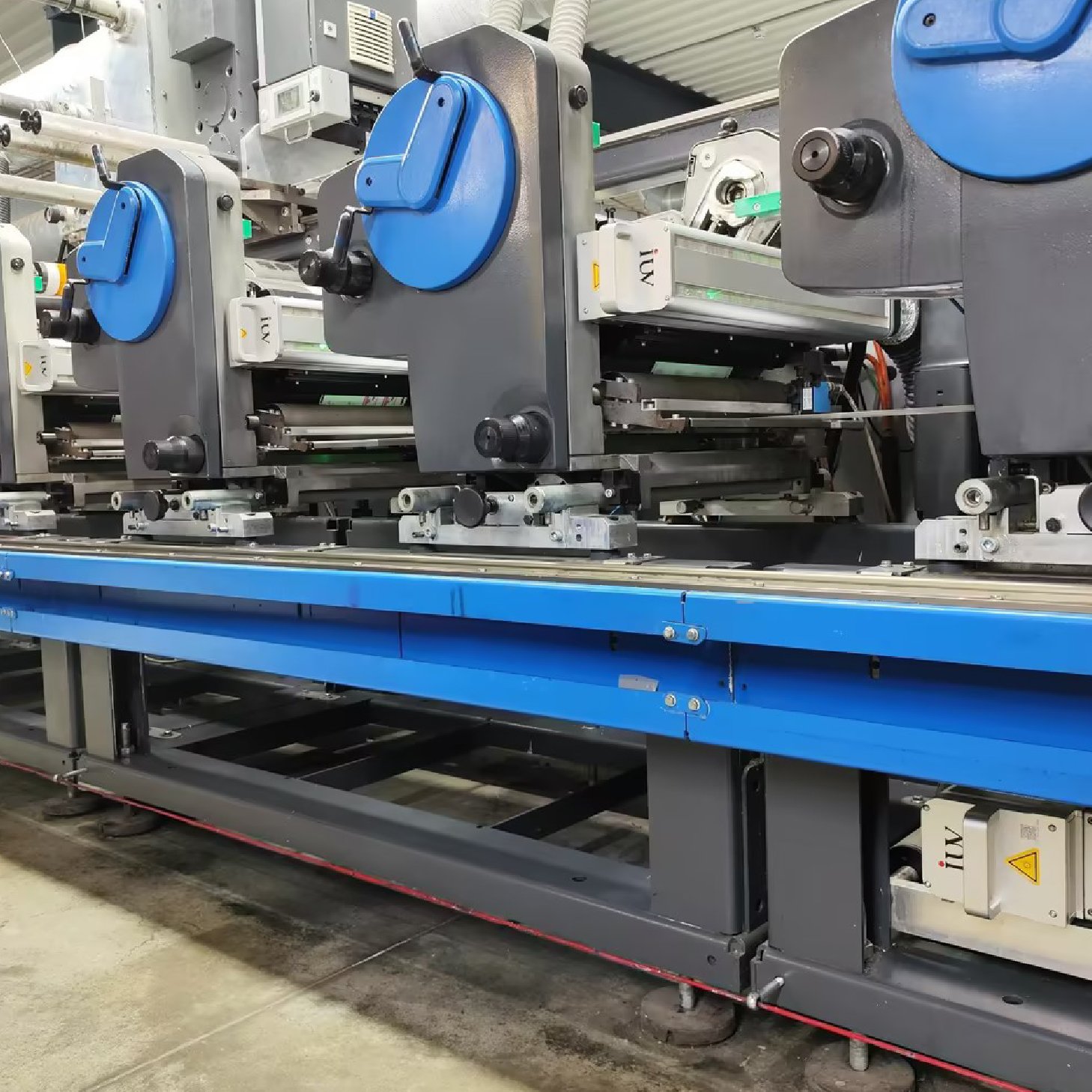
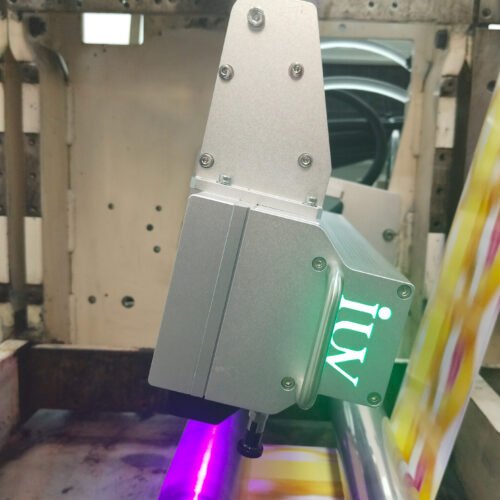
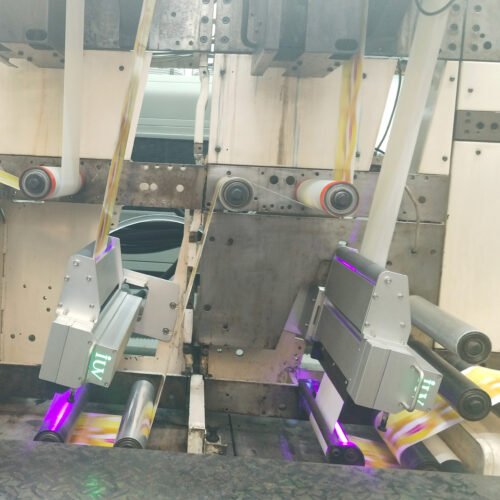
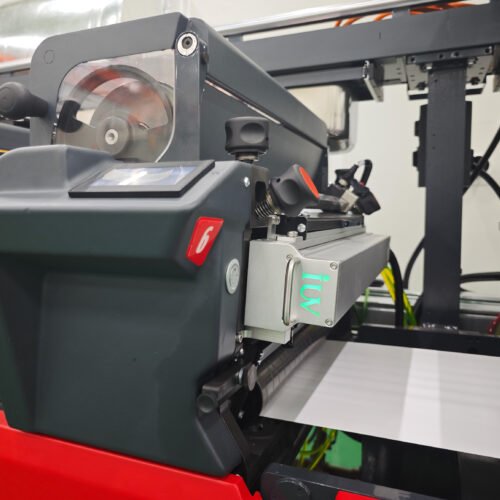
The narrow-web printing sector is constantly seeking innovations that boost efficiency, quality, and versatility. For label printers, achieving superior adhesion and vibrant ink density is paramount. This is where the advancements in LED UV curing technology for flexographic (flexo) printing truly shine. Traditional UV curing methods have long been a staple, but the emergence of LED UV offers distinct advantages that directly impact the critical metrics of adhesion and ink density.
Understanding the Core Challenges in Narrow-Web Printing
Before exploring the benefits of LED UV, it’s helpful to understand the inherent challenges in narrow-web printing, particularly for labels and flexible packaging.
- Substrate Variety: Narrow-web presses handle a vast array of substrates, from highly porous papers to non-porous films like polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), and polyester (PET). Each material presents unique surface energy characteristics that affect ink adhesion.
- High-Speed Production: The demand for faster turnaround times means presses operate at high speeds. This rapid processing can limit the time available for inks to properly bond with the substrate, potentially leading to adhesion issues.
- Ink Film Thickness: Achieving optimal ink density often requires precise control over ink film thickness. Too thin, and the color lacks depth. Too thick, and it can lead to drying problems, smudging, or waste.
- Environmental Considerations: Traditional solvent-based inks raise environmental concerns. UV-curable inks offer a more sustainable alternative, but their curing process is key to performance.
The Mechanics of UV Curing: Traditional vs. LED
Both traditional UV curing and LED UV curing rely on the rapid polymerization of UV-curable inks, coatings, and adhesives when exposed to ultraviolet light. The primary difference lies in the light source.
- Traditional Mercury Lamps: These systems use broad-spectrum mercury vapor lamps. They emit a wide range of UV wavelengths and also generate significant heat and infrared radiation. They require a warm-up period and have a finite lifespan, leading to fluctuating energy output over time.
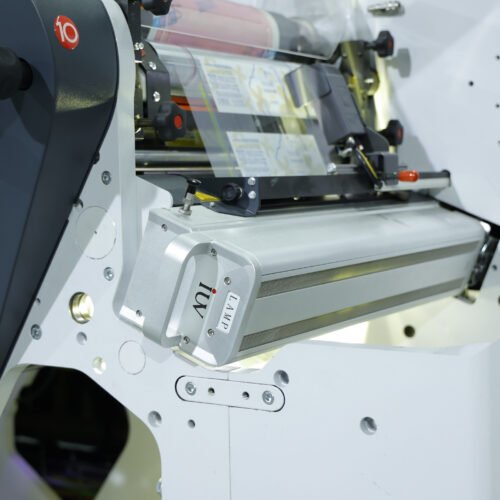
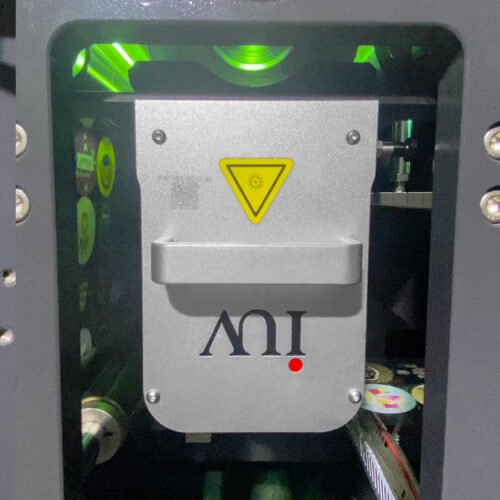
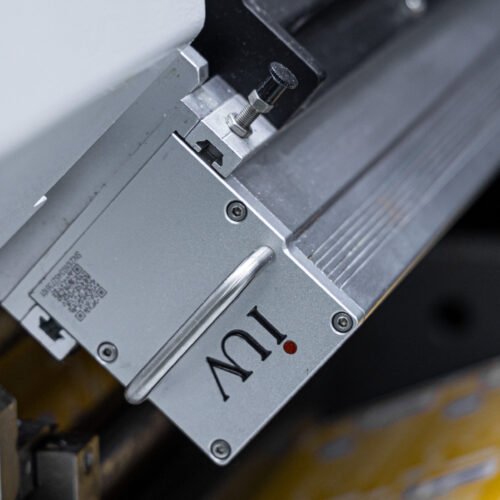
- LED UV Systems: These utilize light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as the UV source. LEDs emit a narrow band of specific UV wavelengths, typically in the UVA spectrum (e.g., 365 nm, 385 nm, 395 nm, 405 nm). They are instant on/off, generate very little heat, and have a much longer operational lifespan.
How LED UV Curing Impacts Adhesion
Adhesion is the strength with which the ink or coating bonds to the substrate. In narrow-web flexo, poor adhesion can lead to labels peeling off products, graphics smudging during handling, or the entire printed piece failing in its intended application. LED UV curing directly influences adhesion in several key ways:
- Controlled Curing Spectrum: Traditional mercury lamps emit a broad spectrum. Some of these wavelengths may not be as efficient for curing specific photoinitiators present in UV inks. LED UV systems offer precisely tuned wavelengths. This targeted spectrum can activate photoinitiators more efficiently, leading to a more complete and robust cure. A thorough cure means the ink polymerizes more effectively, forming stronger chemical bonds with the substrate.
- Reduced Heat and Substrate Distortion: The significant heat generated by mercury lamps can be problematic, especially when printing on heat-sensitive substrates like thin films or certain papers. Excessive heat can cause these materials to shrink, warp, or even degrade. This physical stress can compromise the ink layer and its bond. LED UV’s low heat output preserves substrate integrity, allowing the ink to cure without thermal interference, thereby promoting better mechanical adhesion.
- Surface Energy Activation: While not as pronounced as with some specialized UV systems, the specific wavelengths emitted by LEDs can sometimes have a subtle effect on the substrate surface itself, potentially increasing its surface energy momentarily. This can facilitate better wetting and initial bonding of the ink.
- Consistent Energy Output: Mercury lamps degrade over time, meaning their UV output diminishes. This inconsistency can lead to under-curing and thus weaker adhesion, especially in longer print runs. LEDs maintain a stable and consistent energy output throughout their lifespan, ensuring reliable and repeatable curing conditions and, consequently, consistent adhesion.
How LED UV Curing Enhances Ink Density
Ink density refers to the opacity and richness of the printed color. High ink density is crucial for vibrant graphics, clear text, and effective brand representation on labels. LED UV curing contributes to better ink density through:
- Efficient Photoinitiator Activation: The precise wavelengths of LED UV are highly efficient at activating the photoinitiators in UV-curable inks. This efficient activation leads to faster and more complete polymerization of the ink resins. A fully polymerized ink film is more robust, less porous, and better able to reflect light uniformly, contributing to a denser appearance.
- Reduced Migration and Blooming: Traditional UV curing, especially with higher heat, can sometimes lead to ink migration or “blooming” where components of the ink move to the surface after curing. This can create a hazy appearance and reduce perceived ink density. LED UV’s cooler curing process minimizes these issues, ensuring the ink film remains intact and dense.
- Optimized Ink Film Thickness: While ink formulation plays a major role, the curing process itself is critical. With LED UV, the rapid and efficient cure allows printers to potentially use slightly thinner ink films while still achieving excellent density. This is because the polymerization is so effective that it creates a solid, opaque layer without needing excessive ink volume. Thinner ink films can also lead to cost savings on ink consumption.
- No Solvent Evaporation: UV-curable inks contain no volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that need to evaporate. The entire ink film is converted into a solid polymer. LED UV ensures this solid conversion is complete, leading to a solid, opaque ink film that contributes to high density.
The Practical Advantages for Narrow-Web Flexo Printers
Implementing LED UV technology in narrow-web flexo printing offers tangible benefits beyond just adhesion and density:
- Energy Savings: LEDs consume significantly less energy compared to mercury lamps, leading to lower operating costs.
- Reduced Downtime: Their long lifespan means fewer lamp replacements, and their instant on/off capability eliminates warm-up and cool-down times, increasing press uptime.
- Improved Working Environment: The lack of ozone generation and significantly reduced heat output creates a safer and more comfortable working environment for press operators.
- Versatility: The ability to print on a wider range of substrates, including heat-sensitive ones, expands the application possibilities for narrow-web printers. This includes high-barrier films for food packaging, shrink sleeves, and specialized labels.
- Faster Production Speeds: The efficient curing process of LED UV allows presses to run at higher speeds without compromising ink performance, leading to increased throughput.
Considerations for Transitioning to LED UV
While the benefits are clear, a successful transition to LED UV requires careful consideration:
- Ink and Coating Formulations: Not all traditional UV inks are optimized for LED curing. Printers need to ensure they are using inks and coatings specifically formulated with LED-compatible photoinitiators. These are readily available from major ink manufacturers.
- Press Retrofitting or New Equipment: While many narrow-web presses can be retrofitted with LED UV systems, the decision to invest in new equipment with integrated LED UV technology should be based on production needs and ROI calculations.
- Wavelength Matching: Ensuring the LED output wavelength matches the absorption spectrum of the photoinitiators in the inks is crucial for optimal curing. Reputable suppliers will guide this selection.
- Drying and Curing Stations: The placement and power of the LED UV units need to be configured correctly for the specific press and job requirements.
Conclusion
The integration of LED UV curing technology in narrow-web flexographic printing represents a significant leap forward. For label and packaging converters, the ability to achieve superior adhesion and enhanced ink density is no longer an aspiration but a readily achievable reality. By offering a more controlled, efficient, and sustainable curing process, LED UV systems empower printers to meet and exceed the demands of today’s market, delivering high-quality, durable, and visually striking printed products with greater consistency and cost-effectiveness. The future of narrow-web printing is undoubtedly illuminated by LED technology.