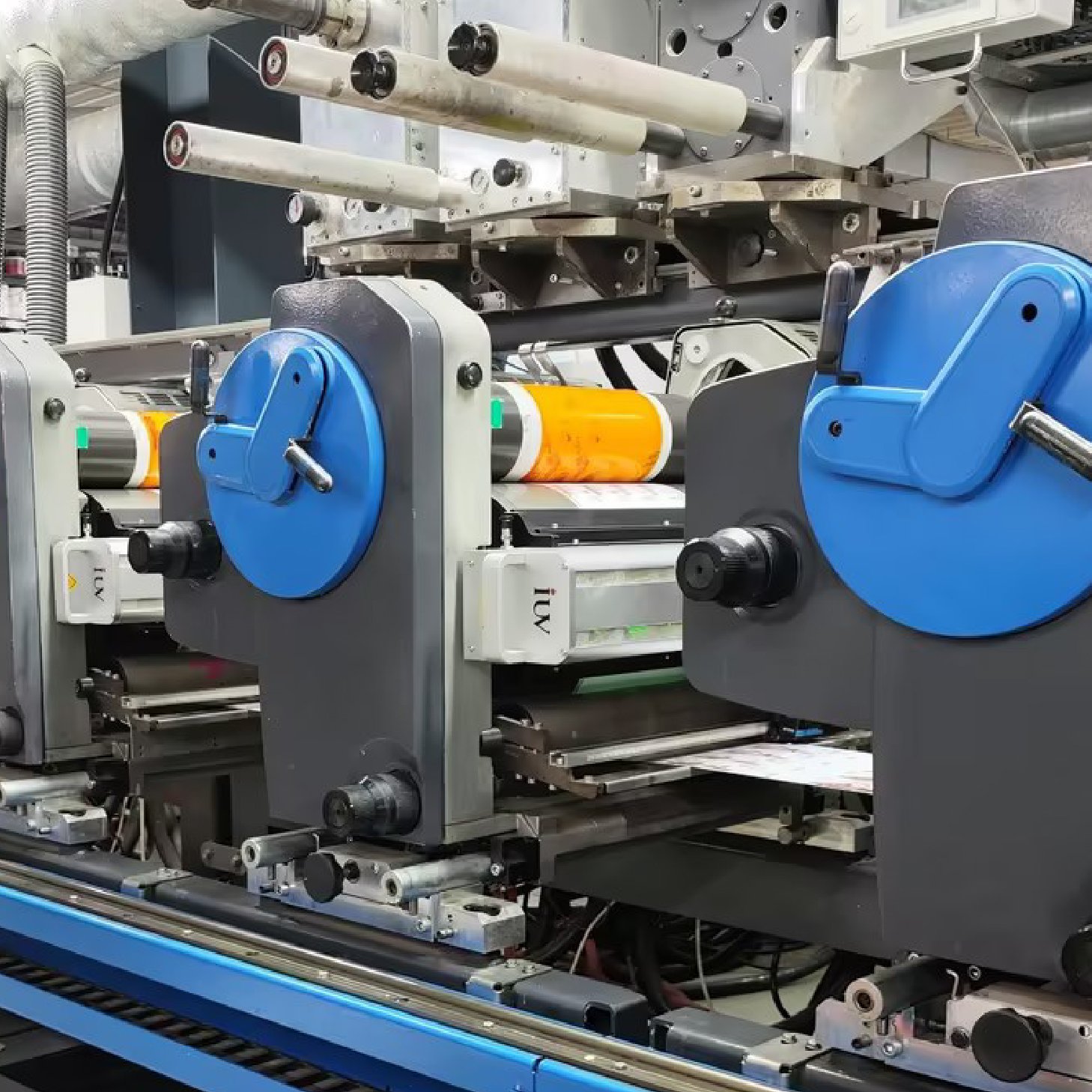
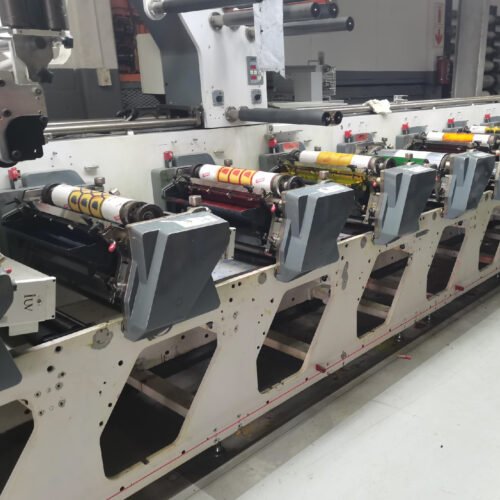
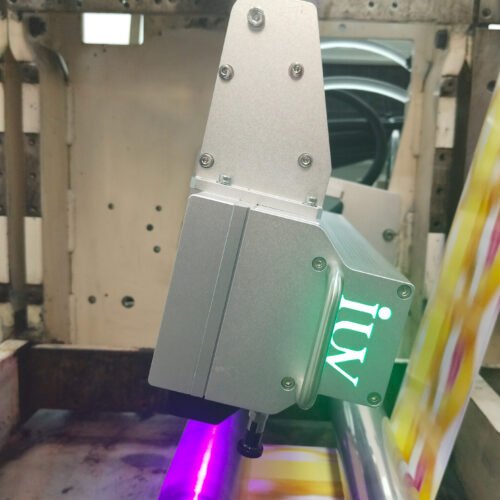
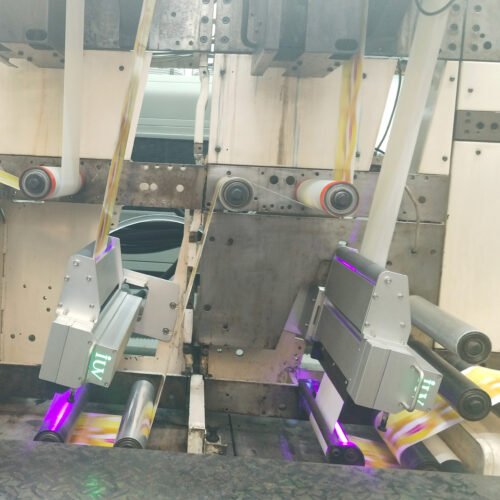
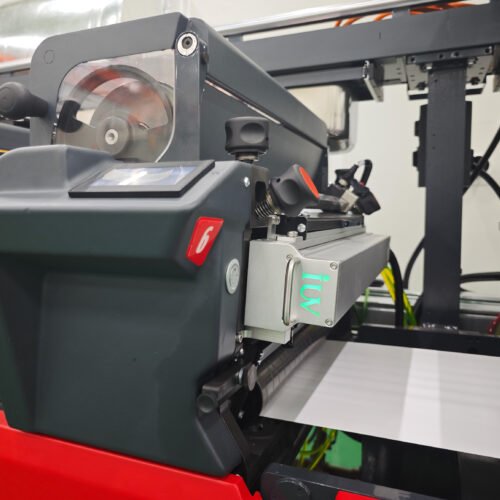
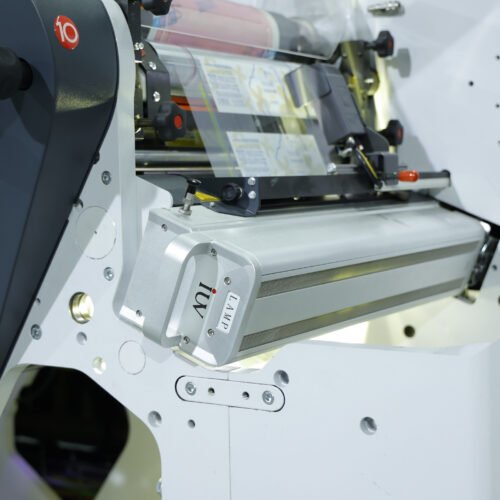
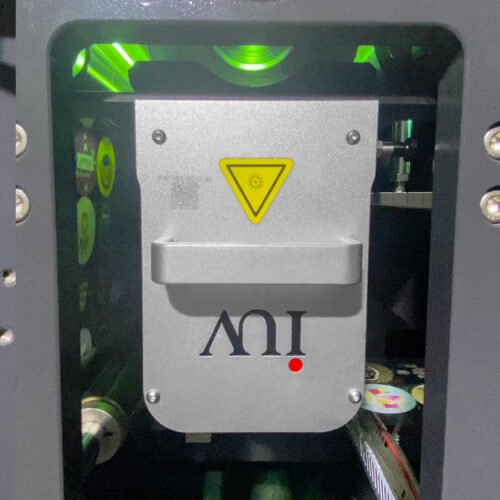
The printing industry is constantly evolving, driven by demands for greater efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced performance. In the narrow-web sector, particularly for labels and flexible packaging, the adoption of LED UV curing technology within flexographic printing systems represents a significant leap forward. These systems offer compelling advantages, not only in terms of energy savings but also in overall production speed and print quality.
Understanding Narrow-Web Flexography
Narrow-web flexography is a high-volume printing process primarily used for producing labels, stickers, and flexible packaging. The “narrow-web” designation refers to the printing substrate, which is typically a roll of flexible material typically less than 20 inches (50 cm) wide. Flexography itself is a versatile printing method that uses a raised relief image on a flexible printing plate. Ink is transferred from an anilox roll to the plate, and then directly to the substrate. Its ability to print on a wide variety of materials, including plastics, films, and foils, makes it ideal for packaging applications.
The Role of UV Curing in Flexography
Traditionally, UV curing systems used in flexography relied on mercury vapor lamps. While effective, these lamps generated considerable heat and consumed a substantial amount of energy. Furthermore, they required a warm-up period and had a finite lifespan, necessitating frequent replacement. The curing process itself involved irradiating the ink with ultraviolet light, causing it to polymerize and dry almost instantaneously. This rapid drying is crucial for high-speed printing, preventing ink smudging and allowing for multiple color stations to be used without interference.
The Advent of LED UV Curing Technology
Light Emitting Diode (LED) UV curing technology has revolutionized the way UV inks are cured in flexographic printing. Instead of a broad spectrum of UV light emitted by mercury lamps, LED systems use diodes that emit UV light at specific wavelengths, precisely matched to the photoinitiators in the UV-curable inks. This targeted approach offers a cascade of benefits.
Energy Efficiency: A Core Advantage of LED Systems
One of the most significant advantages of LED UV curing is its remarkable energy efficiency. Mercury lamps are notoriously power-hungry, often consuming several kilowatts per lamp. They also generate a substantial amount of infrared radiation, which contributes to heat build-up on the substrate and in the printing environment. This heat can cause issues like substrate shrinkage, ink trapping problems, and discomfort for operators.
LED systems, by contrast, are far more energy-efficient. They consume a fraction of the power of their mercury counterparts, often in the range of hundreds of watts rather than kilowatts. This reduction in energy consumption translates directly into lower operational costs for printing businesses. Moreover, LEDs generate very little heat, which reduces the need for energy-intensive cooling systems and minimizes the thermal impact on sensitive substrates. This also leads to a more stable printing environment.
Performance Gains and Enhanced Productivity
Beyond energy savings, LED UV curing systems contribute to significant performance gains and enhanced productivity in narrow-web flexo operations.
1. Instant On/Off Capability: Unlike mercury lamps that require warm-up and cool-down times, LEDs can be switched on and off instantaneously. This is invaluable for job setup and changeovers, as there is no waiting period for the lamps to reach optimal operating temperature. This reduces downtime between jobs, allowing for quicker turnaround times and increased overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
2. Longer Lifespan and Reduced Maintenance: LED UV lamps have an exceptionally long operational lifespan, often rated for tens of thousands of hours. This is significantly longer than the typical lifespan of mercury lamps, which are usually measured in hundreds or a few thousand hours. The extended life of LEDs means fewer lamp replacements, which reduces material costs and minimizes production interruptions due to maintenance.
3. Consistent Output and Predictable Curing: LED systems provide a consistent and stable UV output throughout their lifespan. This leads to more predictable and reliable ink curing from job to job and even within a single long run. Consistent curing ensures optimal ink adhesion, gloss, and resistance properties, contributing to higher print quality and fewer rejected labels or packaging.
4. Reduced Ozone and VOC Emissions: Traditional mercury vapor lamps emit ozone as a byproduct of their operation. This necessitates the use of exhaust ventilation systems to remove ozone from the printing environment, adding complexity and energy costs. LED systems, emitting light at specific wavelengths, generate little to no ozone. This not only improves working conditions but also simplifies ventilation requirements. Furthermore, the efficiency of LED curing contributes to faster and more complete ink polymerization, which can help minimize the potential for volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from the inks themselves.
Impact on Substrate and Ink Versatility
The low heat output of LED UV curing systems opens up new possibilities for printing on a wider range of heat-sensitive substrates. Materials such as thin films, certain plastics, and even some paper stocks that might deform or degrade under the heat of mercury lamps can be safely and effectively printed with LED curing. This expands the application range for narrow-web flexo printers, allowing them to offer services for a broader market.
The development of specialized LED-curable inks has also been crucial. These inks are formulated with photoinitiators that respond optimally to the specific wavelengths emitted by LED lamps. This ensures fast and complete cure, delivering excellent print properties including scratch resistance, chemical resistance, and vibrant color reproduction. Printers can achieve high-quality results across a variety of ink types, including process colors, spot colors, and special effect inks.
Comparison with Other Curing Technologies
While UV curing is prevalent, other technologies exist, such as electron beam (EB) curing and thermal drying. EB curing offers extremely fast cure speeds and excellent properties but requires significant capital investment and shielding due to electron beam radiation. Thermal drying, while suitable for some applications, is slower and can be less efficient for high-speed, multi-color printing on non-absorbent substrates. LED UV flexo systems strike a balance, offering high speeds, excellent cure properties, and a more accessible entry point in terms of cost and operational complexity compared to EB.
Implementing LED UV Flexo Systems
Integrating LED UV curing into a narrow-web flexo press requires careful consideration. This includes:
- Press Compatibility: Ensuring the press is designed or retrofitted to accommodate LED UV units. This involves considerations for space, power supply, and cooling.
- Ink Selection: Choosing inks specifically formulated for LED UV curing at the correct wavelengths.
- Wavelength Matching: Selecting LED units with wavelengths that precisely match the photoinitiators in the chosen inks for optimal cure efficiency.
- Operator Training: Training press operators on the specific requirements and benefits of LED UV technology.
The Future of Narrow-Web Printing
The shift towards LED UV curing in narrow-web flexography is not just a trend; it is a fundamental evolution driven by economic and environmental imperatives. The energy efficiency translates directly to reduced operating costs, making businesses more competitive. The enhanced performance, including faster speeds and reduced downtime, boosts productivity. Furthermore, the lower environmental impact, with reduced energy consumption and ozone generation, aligns with growing corporate sustainability goals. As LED technology continues to advance, offering wider wavelength options and even greater efficiency, its adoption in the narrow-web flexo market is set to accelerate, driving further innovation in label and packaging production.