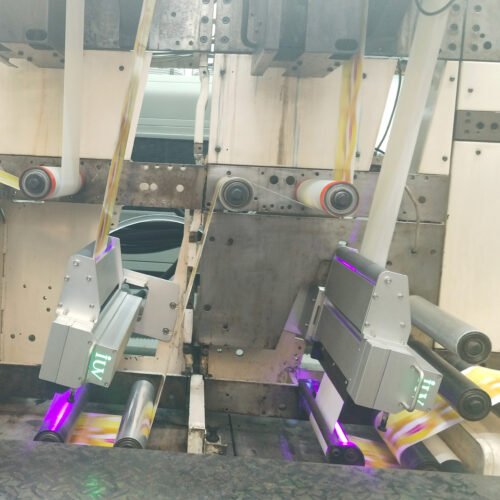
Narrow-web digital printing, a rapidly evolving segment of the label and packaging industry, offers remarkable flexibility and speed. However, its widespread adoption hinges on overcoming a fundamental challenge: substrate compatibility. Unlike conventional printing methods that often rely on specialized inks and treatments for specific materials, digital printing demands a broader range of adaptability. This is particularly true for narrow-web applications, where intricate designs and high print volumes are common.
The variety of substrates used in narrow-web printing is vast. This includes everything from traditional paper and various coated papers to a spectrum of plastic films like PET, BOPP, and PVC, as well as specialty materials such as metallic foils and textured papers. Each of these materials possesses unique surface properties, chemical compositions, and physical characteristics. These differences directly impact how ink adheres, cures, and ultimately, how the final printed product performs.
Understanding the Ink-Substrate Interface
At the heart of substrate compatibility lies the ink-substrate interface. Digital printing inks, whether inkjet or toner-based, are formulated with specific chemistries designed to interact with the printing substrate. For inkjet, these formulations often include pigments or dyes suspended in a liquid carrier, along with additives that control viscosity, surface tension, and drying characteristics. For toner-based digital printing, the “ink” is a dry powder that fuses to the substrate under heat and pressure.
The challenge arises when these inks meet a substrate they weren’t precisely designed for. Surface energy is a critical factor. A substrate with low surface energy, like many plastic films, can repel ink, leading to poor adhesion, dot gain, and an uneven print. Conversely, a substrate with very high surface energy might absorb the ink too quickly, causing it to spread and lose definition.
Beyond surface energy, the substrate’s porosity, chemical inertness, and even its thermal properties play a significant role. Porous materials can wick ink away from the print head or laser, resulting in faded images. Chemically reactive substrates can interact with ink components, causing discoloration or degradation of the ink film. Furthermore, some digital printing processes involve heat, and substrates that cannot withstand these temperatures can warp or melt, leading to print defects and potential press damage.
The Limitations of Traditional Approaches
Historically, print service providers have relied on several strategies to address substrate compatibility. Pre-treatment of substrates, such as corona discharge or plasma treatment, is a common method to increase surface energy and improve ink receptivity. However, these processes add complexity and cost to the workflow. They also require careful control and can be challenging to implement consistently across different job types and production lines.
Another approach involves using specialized inks designed for specific substrates. While effective, this can lead to a large and costly ink inventory. Managing these different ink sets, ensuring proper cleaning between runs, and avoiding cross-contamination adds further operational burdens. For narrow-web printers operating with tight margins, these limitations can be a significant barrier to efficiency and profitability.
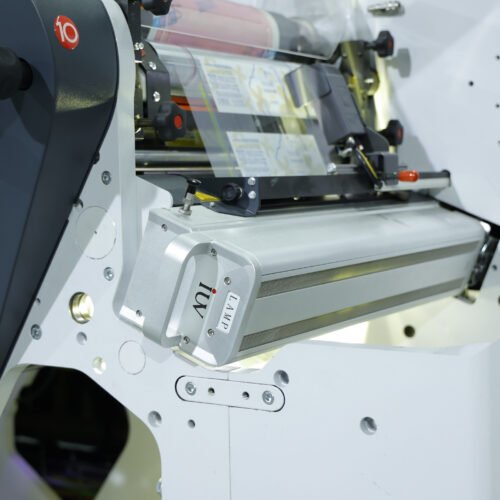
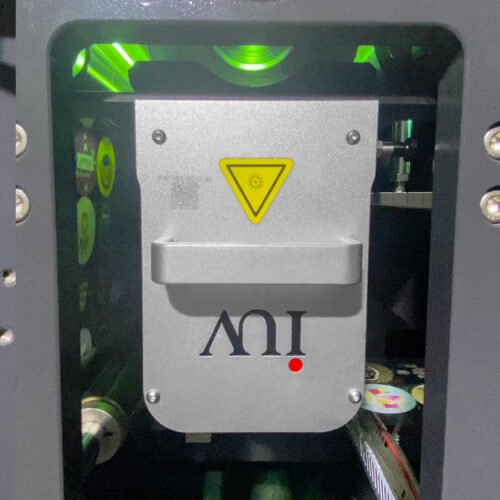
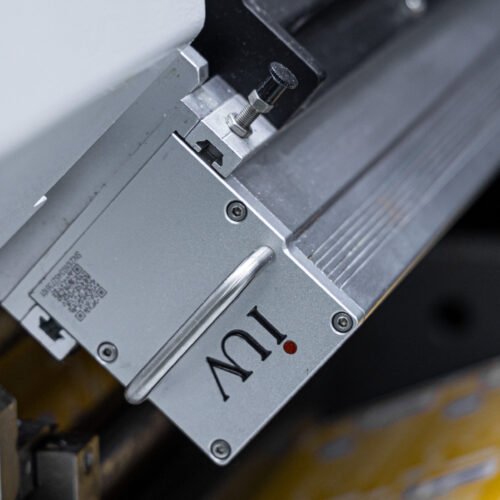
Enter LED UV Curing: A Game Changer
This is where LED UV curing technology emerges as a pivotal solution for substrate compatibility challenges in narrow-web digital printing. Unlike traditional mercury UV lamps, LED UV lamps emit light at specific wavelengths, which are precisely matched to the photoinitiators within UV-curable inks. This targeted energy transfer offers several advantages.
First and foremost, LED UV curing is a “cold cure” technology. The heat generated by LED lamps is significantly lower than that of mercury lamps. This is a major benefit when printing on heat-sensitive substrates like thin films or some papers. The reduced heat minimizes the risk of substrate deformation, shrinkage, or delamination, ensuring dimensional stability and print integrity.
Secondly, the precise wavelength control of LED UV lamps allows for more efficient and complete ink curing. This rapid, on-demand curing process locks the ink onto the substrate’s surface, forming a durable and vibrant print. The ink doesn’t have a chance to migrate or absorb excessively into the substrate before it’s cured. This leads to sharper dots, brighter colors, and superior print quality, even on challenging low-surface-energy materials.
Overcoming Substrate Hurdles with LED UV
The synergy between LED UV curing and ink formulation is key to unlocking broad substrate compatibility. Modern UV-curable inks are engineered with advanced chemistry to work effectively with LED curing systems. These inks often incorporate high-performance photoinitiators that are highly responsive to the specific wavelengths emitted by LED lamps.
For difficult-to-print substrates like polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP), which are inherently low in surface energy, the right combination of LED UV ink and curing power can achieve excellent adhesion without the need for extensive pre-treatment. The ink’s chemistry is designed to “wet” the substrate surface, and the rapid LED UV cure then instantly bonds the ink to it.
Furthermore, the versatility of LED UV inks extends to a wide array of specialty substrates. Metallic foils, for instance, can be printed with high gloss and excellent adhesion, preserving their reflective properties. Textured papers, with their irregular surfaces, can be printed with remarkable detail and clarity, as the ink cures quickly on the surface, preventing excessive spread into the valleys of the texture.
Practical Strategies for Success
To maximize substrate compatibility in your narrow-web digital printing operations using LED UV technology, consider these practical strategies:
- Ink and Substrate Matching: Work closely with ink manufacturers to select UV inks specifically formulated for LED curing and the substrates you intend to print on. Provide them with detailed information about your substrates, including their composition and surface energy if known.
- Curing System Optimization: Ensure your LED UV curing system is correctly configured. This includes aligning the wavelength of the LEDs with the photoinitiators in your inks and setting the appropriate power output and exposure time. Even small adjustments can significantly impact adhesion and cure quality.
- Pre-treatment Evaluation: While LED UV curing reduces the reliance on pre-treatment, it may still be beneficial for extremely challenging substrates or when aiming for the highest levels of durability. Evaluate if minimal pre-treatment, such as a light corona, could further enhance results without adding excessive complexity.
- Thorough Testing and Validation: Before committing to a full production run, always conduct rigorous testing on your intended substrates. Print sample swatches and perform adhesion tests (e.g., cross-hatch tape test), rub tests, and any other relevant performance evaluations for the end-use application.
- Consider Ink Properties: Beyond adhesion, think about other ink properties like flexibility, chemical resistance, and lightfastness. LED UV inks are generally quite robust, but specific formulations will offer different levels of performance. Choose an ink that meets all the application requirements.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature and humidity in the printing environment can subtly affect substrate behavior and ink performance. Maintain a stable printing environment to ensure consistent results.
The Future is Flexible and Cured
The challenges of substrate compatibility in narrow-web digital printing are undeniable, but they are not insurmountable. The advent and refinement of LED UV curing technology have provided print service providers with a powerful tool to expand their capabilities. By understanding the interplay between inks, substrates, and curing methods, and by adopting a strategic approach to testing and optimization, you can unlock new opportunities and achieve exceptional print quality across a diverse range of materials. This technology empowers a more agile, efficient, and versatile approach to narrow-web printing, setting the stage for future innovations.