Ink migration refers to the unwanted transfer of ink components from the printed substrate to the surface of another material, or even into the product itself. This phenomenon is a significant concern, particularly in food packaging and pharmaceutical applications, where even trace amounts of migrating substances can pose health risks and compromise product integrity.
Several factors influence ink migration:
- Ink Formulation: The chemical composition of the ink, including its binder, pigments, and additives, plays a crucial role. Some components are inherently more prone to migration than others.
- Substrate Properties: The type of material being printed on, such as paper, film, or foil, affects its porosity and surface energy, influencing how well the ink adheres and how easily components can leach out.
- Printing Process: The specific printing method and the conditions under which it operates, including temperature, pressure, and curing method, all contribute to the likelihood of migration.
- Post-Print Handling: Factors like stacking, winding, and storage conditions can also impact ink migration.
The Role of UV Curing Technology
Traditional curing methods, like thermal drying, often rely on evaporation to remove solvents from the ink. This process can leave behind uncured or partially cured ink components that are more susceptible to migration.
UV (Ultraviolet) curing, on the other hand, utilizes high-intensity UV light to initiate a photochemical reaction within specially formulated inks, coatings, and adhesives. This reaction causes rapid polymerization, transforming the liquid ink into a solid, cross-linked film.
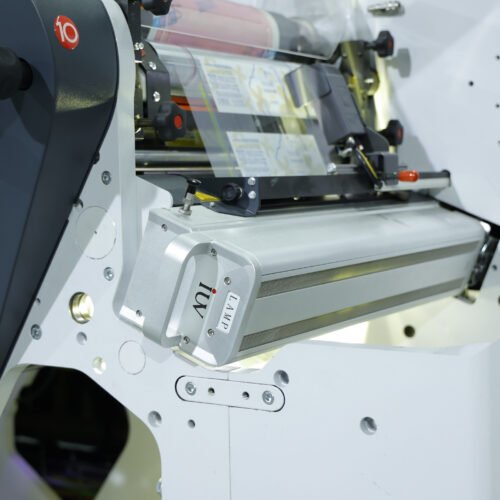
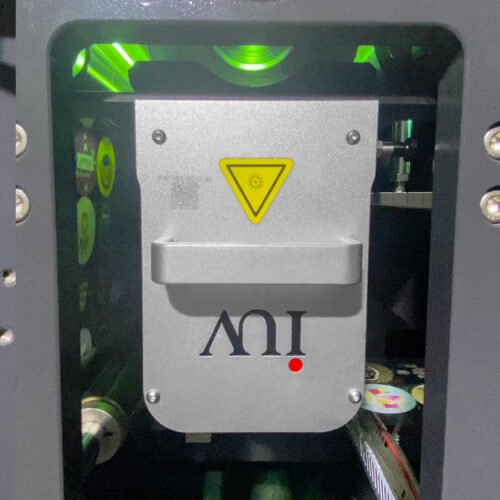
Introducing LED UV Curing Systems
While traditional UV curing lamps (mercury-vapor lamps) have been effective, they come with several drawbacks:
- High Energy Consumption: They require significant amounts of energy to operate.
- Heat Generation: They produce a substantial amount of heat, which can be detrimental to heat-sensitive substrates and increase energy costs for cooling.
- Lamp Replacement and Maintenance: Mercury lamps have a limited lifespan and require frequent replacement and disposal, which can be costly and environmentally challenging.
- Ozone Production: Some traditional UV lamps produce ozone, a harmful gas that requires ventilation systems.
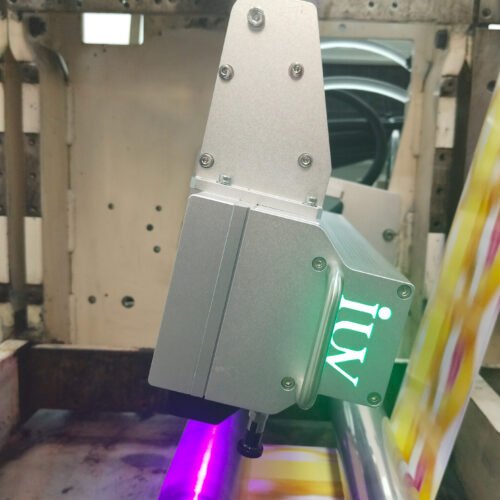
LED UV curing systems offer a compelling alternative. They utilize Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) to emit UV light at specific wavelengths. This technology brings a host of advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume significantly less power compared to traditional UV lamps, leading to substantial cost savings.
- Low Heat Emission: LEDs generate much less heat, making them ideal for printing on delicate or heat-sensitive materials without causing distortion or damage.
- Long Lifespan: LEDs have a considerably longer operational life, reducing downtime and maintenance costs associated with lamp replacements.
- Instant On/Off: LEDs can be switched on and off instantly, eliminating warm-up times and further enhancing energy efficiency.
- Targeted Wavelengths: LEDs can be manufactured to emit specific UV wavelengths, allowing for optimized curing of different ink formulations.
- No Ozone Production: LED systems typically do not produce ozone, simplifying ventilation requirements.
How LED UV Curing Mitigates Ink Migration Risks
The fundamental principle behind LED UV curing’s effectiveness in reducing ink migration lies in its ability to achieve a more complete and robust cure.
- Complete Polymerization: LED UV systems, when properly matched with the ink formulation, ensure that the monomers and oligomers in the ink undergo thorough polymerization. This cross-linking process creates a tightly bound, solid ink film where individual components are locked in place. This significantly reduces the likelihood of unreacted or loosely bound components leaching out.
- Surface and Through Cure: The specific wavelengths emitted by LEDs can be chosen to optimize both surface cure and through cure. A good surface cure prevents immediate rub-off and enhances scuff resistance. A thorough through cure ensures that the entire ink layer, from the substrate interface to the surface, is fully solidified, minimizing opportunities for migration.
- Reduced Thermal Stress: As mentioned earlier, LED UV curing generates less heat than traditional UV systems. This lower thermal stress is particularly beneficial for flexible substrates like films and foils used in narrow web label printing. Excessive heat can sometimes cause plasticizers or other volatile components within the substrate or ink to become more mobile, increasing migration potential. By keeping temperatures down, LED UV curing helps maintain the integrity of both the substrate and the cured ink film.
- Enhanced Adhesion: A complete cure achieved with LED UV technology often results in improved adhesion between the ink and the substrate. Stronger adhesion means the ink film is less likely to delaminate or break down, further preventing the release of ink components.
- Controlled Wavelengths: Different ink formulations are designed to cure most efficiently at specific UV wavelengths. LED systems can be configured with LEDs that emit these precise wavelengths, ensuring optimal energy transfer for rapid and complete curing. This targeted approach minimizes the energy wasted on wavelengths that are not absorbed by the photoinitiators in the ink, leading to a more efficient and thorough cure.
Applications in Different Printing Processes
The benefits of LED UV curing for reducing ink migration are widely applicable across various printing technologies used in label production:
Narrow Web Flexographic Printing
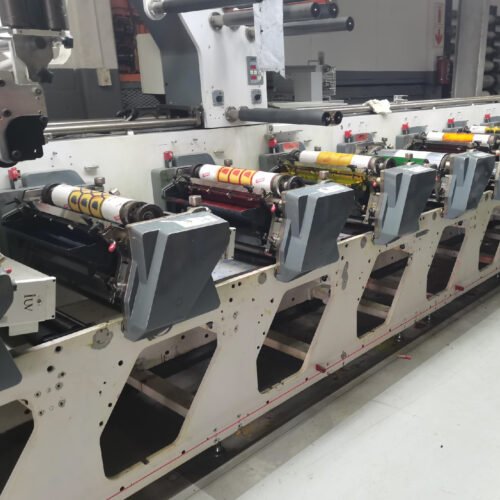
Flexography is a dominant force in label printing. In this process, a flexible relief plate transfers ink to the substrate. Narrow web flexo presses are often equipped with multiple print stations, allowing for multi-color jobs.
- Process: Flexo inks, often water-based or UV-curable, are applied to the substrate.
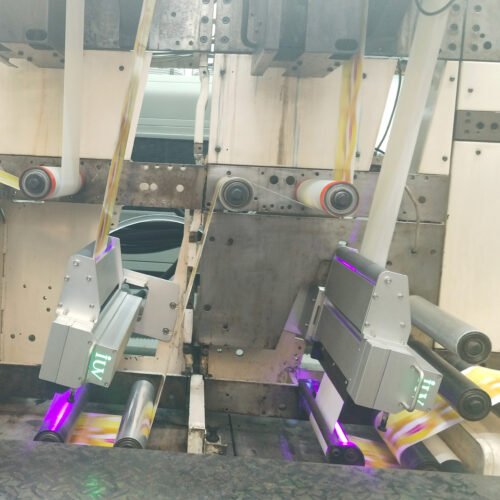
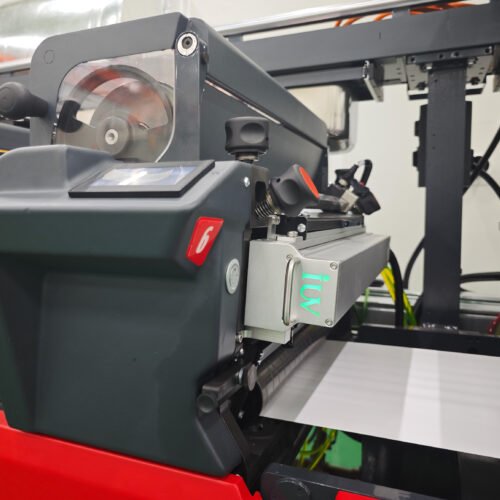
- LED UV Benefit: Installing LED UV curing units between print stations or at the end of the press ensures that each ink layer is fully cured before the next color is applied or before the roll is finished. This prevents inter-coat contamination and ensures a robust final print, significantly lowering migration risks, especially for food-grade labels where compliance with regulations like the Swiss Ordinance and EU regulations is paramount. The ability to print on a wider range of substrates, including sensitive films and foils, without excessive heat is a major advantage.
Offset Lithographic (Sheet-fed and Web) Printing for Labels
While more common for commercial printing, offset lithography is also used for certain types of labels, particularly those requiring high-quality graphics and fine detail.
- Process: Offset printing uses a flat plate to transfer ink to a blanket, which then transfers it to the substrate.
- LED UV Benefit: For label applications utilizing offset printing, integrating LED UV curing can provide a very durable and well-cured ink film. This is especially important for labels that might be handled extensively or exposed to various environmental conditions. The fast curing speed enabled by LED UV allows for immediate post-processing and finishing, reducing the time the printed material spends in a state where migration could potentially occur.
Screen Printing for Specialty Labels
Screen printing is known for its ability to lay down thick ink films, making it suitable for durable labels, control panels, and labels requiring special effects.
- Process: Ink is pushed through a mesh screen onto the substrate.
- LED UV Benefit: Thick ink films can sometimes be challenging to cure completely with traditional methods, increasing the risk of migration. LED UV curing, with its ability to penetrate thicker layers (depending on ink formulation and wavelength), can achieve a full cure throughout the ink deposit. This ensures that even in these thicker applications, the ink components are fully locked into the polymer matrix, minimizing migration potential and enhancing the overall durability and safety of the label.
Key Considerations for Implementing LED UV Curing for Migration Control
To effectively leverage LED UV curing for reducing ink migration, several factors need careful consideration:
- Ink Compatibility: Not all existing UV inks are optimized for LED curing. It is crucial to work with ink manufacturers to select or develop LED-curable inks specifically formulated for the target wavelengths of the chosen LED system. These inks will contain photoinitiators that efficiently absorb the LED emissions.
- Wavelength Selection: Different LED systems emit UV light in various wavelength bands (e.g., 365 nm, 385 nm, 395 nm, 405 nm). The choice of wavelength should align with the absorption spectrum of the photoinitiators in the selected ink. A mismatch can lead to incomplete curing and increased migration risks.
- Irradiance and Dose: Irradiance refers to the power density of the UV light delivered to the ink surface, while dose is the total amount of UV energy applied (irradiance multiplied by exposure time). Both need to be sufficient to achieve a complete cure. This often involves selecting appropriate LED units with adequate power output and ensuring the correct web speed or exposure time.
- Substrate Type: As discussed, the substrate’s properties (porosity, color, thickness) can influence UV light penetration and absorption. Dark or highly absorbent substrates may require higher energy doses or different wavelengths to ensure adequate through cure.
- Application Requirements: For regulated applications like food packaging, specific migration limits must be met. This often necessitates rigorous testing and certification of the printed materials. Choosing an LED UV curing system as part of a well-controlled printing process is a vital step in achieving compliance.
Conclusion
Reducing ink migration is a paramount concern in the printing industry, especially for labels used in sensitive applications. LED UV curing systems offer a technically superior and environmentally friendly solution. By enabling faster, more efficient, and more complete ink polymerization with reduced thermal impact, LED UV technology fundamentally strengthens the ink film. This enhanced cure minimizes the mobility of ink components, thereby significantly lowering the risk of migration. When implemented with careful consideration of ink compatibility, wavelength selection, and process parameters, LED UV curing systems are an indispensable tool for printers aiming to produce safe, compliant, and high-quality labels.