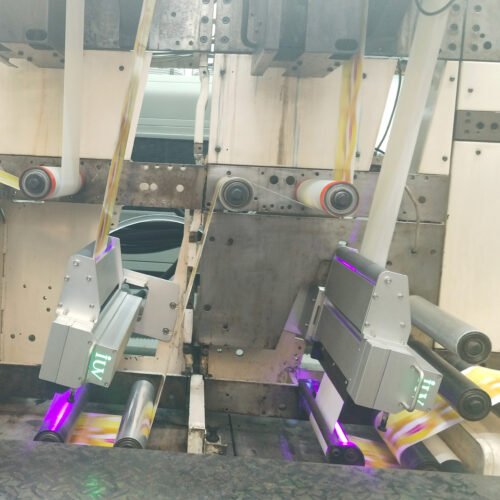
Understanding LED UV curing is vital for modern printing operations. This technology offers significant advantages in speed, energy efficiency, and reduced environmental impact. However, achieving optimal results hinges on carefully controlling several key parameters. In the demanding fields of label printing, flexographic printing, offset printing, and narrow web printing, these parameters directly influence both the efficiency of the curing process and the long-term reliability of the printed product.
Irradiance: The Foundation of Curing Speed
Irradiance, often measured in milliwatts per square centimeter (mW/cm²), is perhaps the most fundamental parameter. It quantifies the amount of UV energy delivered to the ink or coating surface per unit of time. Higher irradiance levels generally lead to faster curing speeds. This is particularly important in high-speed printing environments like narrow web and flexographic presses where production throughput is paramount.
In flexographic and narrow web label printing, where substrates are often thin and sensitive, achieving sufficient irradiance without overheating is a delicate balance. For offset printing, especially on non-porous substrates, higher irradiance can ensure complete through-cure, preventing issues like ink rub-off and ensuring good adhesion. The specific energy requirements will vary greatly depending on the UV-curable ink or coating formulation being used.
Dose: The Total Energy Delivered
While irradiance is about the rate of energy delivery, dose refers to the total amount of UV energy delivered over the exposure time. It’s calculated by multiplying irradiance by the exposure time. Dose is typically measured in joules per square centimeter (J/cm²).
For a given ink system, there’s an optimal dose required for complete polymerization. Too little dose results in under-cured ink, leading to poor adhesion, scratch resistance, and potential migration issues. Too much dose, while ensuring cure, can sometimes lead to substrate degradation or yellowing, especially with heat-sensitive materials common in label printing. Ensuring the correct dose is crucial for consistent print quality and product performance across all printing types.
Wavelength: Matching Energy to Chemistry
LED UV lamps emit energy at specific wavelengths. These wavelengths are critical because they must match the absorption spectrum of the photoinitiators within the UV-curable ink or coating. If the emitted wavelength doesn’t align with the photoinitiator’s absorption peak, the energy transfer will be inefficient, and curing will be slow or incomplete.
Most UV-curable inks utilize photoinitiators that absorb in the UVA range (320-400 nm). Different LED configurations can emit narrow bands within this range, such as 365 nm, 385 nm, 395 nm, or 405 nm. For example, specific formulations for food packaging labels might be designed to cure efficiently with particular LED wavelengths to ensure compliance with migration standards. In offset and flexographic printing, selecting the right LED wavelength that complements the ink chemistry is key to achieving maximum cure speed and depth.
Uniformity: Consistent Illumination Across the Web
Uniformity refers to how evenly the UV energy is distributed across the entire width of the printed web. Inconsistent irradiance across the print area can lead to patchy curing. Some areas might be over-cured, while others are under-cured. This is a critical factor in narrow web and flexographic printing where print areas can be extensive and variations can easily occur.
Poor uniformity can manifest as differences in gloss, adhesion, or color density across the label or printed material. Achieving high uniformity requires well-designed LED lamp arrays and careful consideration of reflector design and distance to the substrate. Modern LED curing systems are engineered to deliver highly uniform irradiance profiles, ensuring consistent quality from edge to edge.
Temperature Management: Preventing Substrate and Ink Degradation
While LED UV curing is generally considered a “cool cure” technology compared to traditional mercury vapor lamps, heat is still generated. The energy delivered can increase the temperature of both the ink and the substrate. For heat-sensitive substrates commonly used in label printing, such as certain plastics or foils, excessive heat can cause deformation, shrinkage, or delamination.
Effective thermal management systems, including adequate airflow and heat sinks within the LED curing unit, are essential. Monitoring substrate temperature during printing can help prevent these issues. In high-speed flexographic and offset applications, efficient heat dissipation ensures that the curing process doesn’t compromise the integrity of the substrate.
Exposure Time: The Dance with Speed
Exposure time is directly linked to the printing press speed. As press speeds increase in narrow web and flexographic printing, the time the ink or coating spends under the UV lamps decreases. To maintain adequate dose and ensure complete cure, the irradiance level must be increased proportionally.
This relationship highlights the interconnectedness of these parameters. A press operator might increase speed to boost productivity. However, this necessitates a corresponding increase in irradiance from the LED UV system. If the LED system cannot deliver the required irradiance, the operator may have to reduce speed or accept a compromised cure, impacting reliability and print quality.
System Design and Maintenance: Ensuring Long-Term Performance
Beyond the immediate curing parameters, the design and ongoing maintenance of the LED UV curing system play a significant role in efficiency and reliability. This includes the quality of the LED chips, the driver electronics, the cooling system, and the protective optics.
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning optics to remove ink or debris, checking connections, and verifying irradiance levels with a radiometer, is crucial. A system that is well-maintained will consistently deliver the specified irradiance and wavelength, ensuring predictable curing performance over its lifespan. For businesses in competitive markets like label and narrow web printing, consistent performance directly translates to reduced waste and greater customer satisfaction.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach
In summary, achieving efficient and reliable LED UV curing in label, flexographic, offset, and narrow web printing requires a holistic approach to managing several key parameters. Irradiance, dose, wavelength, uniformity, temperature, and exposure time all interact to determine the success of the curing process. By understanding and meticulously controlling these factors, printers can unlock the full potential of LED UV technology, leading to faster production, improved print quality, and more durable, reliable printed products. Regular system maintenance and a well-designed curing unit are the cornerstones of sustained high performance.