The label printing industry has undergone transformative advancements with UV curing and lamination technologies. These methods address critical demands for high-quality, durable, and visually striking labels while aligning with sustainability goals. This article delves into the science, applications, and optimization strategies for UV curing and lamination in modern label production.
1. UV Curing: A Game-Changer in Label Printing
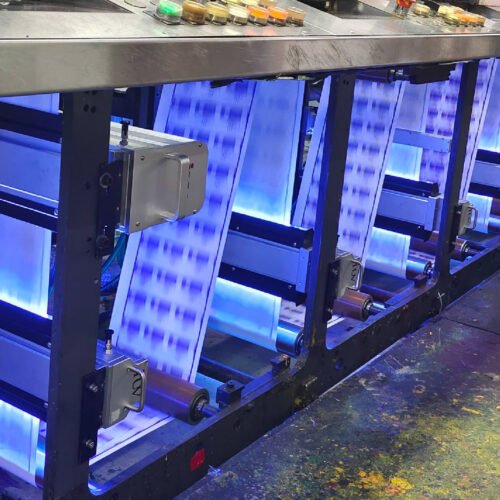
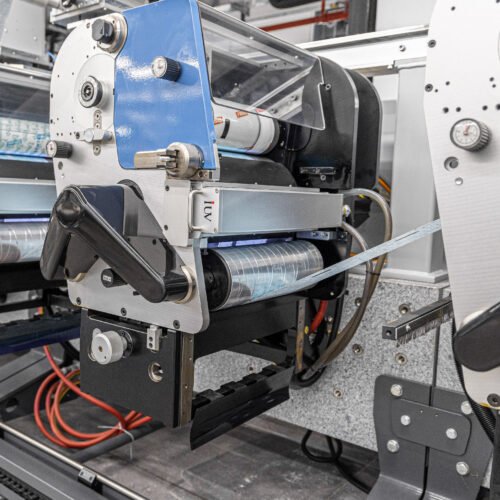
UV curing uses ultraviolet light to instantly dry inks, coatings, and adhesives through photochemical reactions. Unlike traditional heat-based drying, UV curing eliminates solvent evaporation, reducing energy consumption and volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions.
Key Advantages:
- Speed and Efficiency: UV curing enables rapid drying (within seconds), boosting production throughput by up to 50% compared to conventional methods.
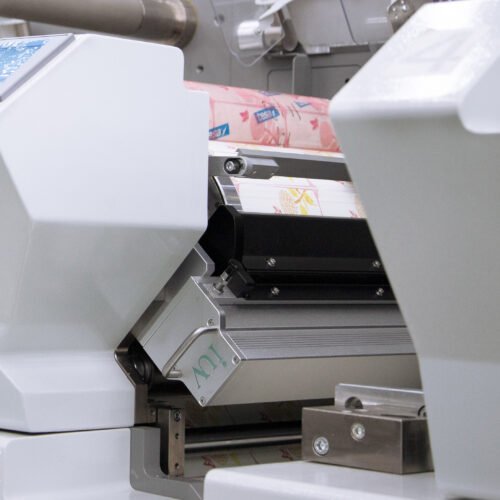
- Superior Print Quality: UV-cured inks retain vibrant colors and sharp details, as they do not absorb into substrates. This ensures consistent gloss and scratch resistance.
- Versatility: Compatible with diverse materials, including paper, plastic, metal, and glass, UV curing supports flexible packaging, cosmetics, and industrial labels.
Optimization Tips:
- Ink Selection: Use UV-specific inks with photoinitiators to ensure efficient light absorption and curing.
- Lamp Calibration: Adjust UV light intensity to match substrate and ink requirements, preventing under- or over-curing.
- Cooling Systems: Integrate advanced cooling mechanisms to manage heat-sensitive materials during high-speed processes.
2. Lamination Techniques for Enhanced Label Durability
Lamination involves bonding a protective film to printed labels, improving resistance to moisture, abrasion, and UV exposure. Common types include gloss, matte, and specialty films (e.g., scratch-resistant or textured).
Critical Applications:
- High-End Packaging: Matte lamination adds a premium feel, while gloss films enhance color vibrancy for luxury products.
- Functional Protection: Films with anti-counterfeiting features or tamper-evident properties are ideal for pharmaceuticals and electronics.
Innovative Approaches:
- UV-Based Lamination: Combining UV curing with lamination reduces processing steps. For example, UV coatings can replace traditional films, offering faster curing and reduced material waste.
- Reverse UV: This technique creates contrasting gloss/matte effects by leveraging UV varnish incompatibility, eliminating the need for additional films.
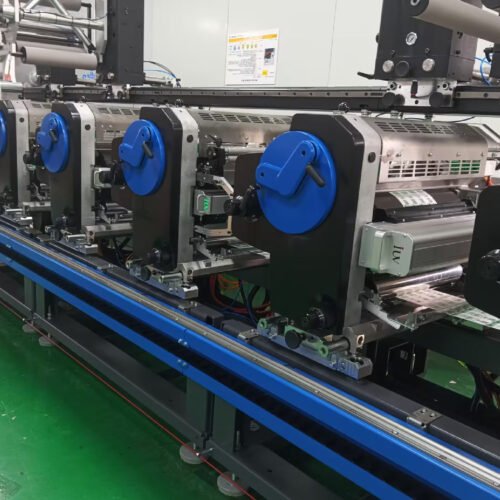
3. Synergy Between UV Curing and Lamination
Integrating UV curing with lamination streamlines production and elevates label performance:
- Reduced Downtime: UV-cured inks stabilize on press, minimizing cleanup during label lamination.
- Eco-Friendly Solutions: UV technology’s solvent-free process and energy efficiency align with circular economy principles.
- Advanced Textures: UV matte and embossed effects are achievable through hybrid workflows, enhancing tactile appeal for cosmetics and beverages.
Future Trends and Sustainability
- LED UV Systems: Energy-efficient LED lamps extend equipment lifespan and lower operational costs.
- Biodegradable Films: Research into compostable lamination materials aims to reduce plastic waste.
- Smart Labels: UV-cured conductive inks enable RFID and NFC integration for track-and-trace applications.
UV curing and lamination are pivotal to modern label printing, offering unmatched quality, efficiency, and sustainability. By adopting optimized workflows and innovative materials, businesses can meet evolving market demands while reducing environmental impact.